Effect-directed analysis of a water sample
For more than 10 years effect-directed analysis in combination with TLC has been used and advocated at the Laboratory for Operation Control and Research of Zweckverband Landeswasserversorgung in Langenau [1]. It began with the Aliivibrio fischeri inhibition assay for the detection of baseline toxicity. Now three more bioassays (end points: estrogenic, antibiotic and neurotoxic effects) have been applied. The method is used as a fast monitoring tool for investigation of raw and drinking water. Subsequently a method is described, which was developed in cooperation with Dr. Wolfgang Schulz and Dr. Rudi Winzenbacher (same institution) and Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Schwack, University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart.
Introduction
Through increasing influence of humans, the environment more and more gets polluted with anthropogenic trace substances. Many of these substances are not characterized and their effects on humans and the ecosystem are only inadequately clarified. Therefore it is very important to evaluate the eco(toxicological) relevance of this multitude of substances, classifying relevant from less relevant ones. Here, effect-directed analysis (EDA) can make a contribution as a combination of fractionation, bioassay and chemical analysis.
For fractionation of EDA, HPTLC has proven to be a particularly suitable method. In comparison to HPLC, HPTLC is an open separation system, thereby separated substances are solvent-free and the following in-vitro-bioassay can be performed directly. However, in comparison to HPLC, this method is limited due to the lower separation efficiency. To increase the separation efficiency of HPTLC, in this work a two-dimensional (2D) separation strategy with effect-directed detection was developed.
In the presented method, zones with detectable effect are eluted with the TLC-MS interface and the respective eluate (200 μL) is collected into a CBS 121 3 sample vial. The acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibition assay for the detection of neurotoxic effects was performed in both separation dimensions. Through this selective procedure, fractions without AChE-inhibiting effects could be excluded after the first separation dimension (1D) and only the effective fractions were transferred for separation in the second dimension.
Standard solutions
For evaluation of the mobile phases, five standards mixed in methanol with a respective concentration of 10 ng/μL were applied. Additionally, a mix with 50 acetylcholinesterase (AChE)-inhibiting substances for spiking of a surface water sample with a concentration of 10 ng/μL of each substance was prepared.
Chromatogram layer
HPTLC LiChrospher silica gel 60 F254S plates (Merck) were immersed twice in 2-propanol for 20 min. After drying at 120 °C the plates were predeveloped to the top edge with acetonitrile. Finally, the plates were heated again to 120 °C for 20 min.
Sample application
Bandwise application with Automatic TLC Sampler (ATS 4), band length 6 mm, distance from the lower edge 8 mm, distance from left edge 20 mm, application volume for standard solutions and spiked surface water sample 10 μL (first development) and 200 μL of collected fractions (second development)
Chromatography
First development is done in the AMD 2 with gradient (16 steps) up to a total migration distance of 80 mm. Isocratic development in the 2nd dimension is performed in the Automatic Development Chamber (ADC 2) with chamber saturation (15 min). The plate is activated for 1 min with a molecular sieve, preconditioned for 30 s, developed up to 70 mm and then dried (20 min with cold air).
AChE inhibition assay
The pH was adjusted to 7.5 by placing the HPTLC-plate in a NH3 vapor saturated twin through chamber, followed by drying with vacuum for 10 min. Then the plate was immersed with the Chromatogram Immersion Device in the AChE solution (0.05 M Tris-HCl buffer, pH 7.8, with 0.1 % bovine serum albumin), dipping speed 2 cm/s, dipping time 2 s. After subtraction of the abundant solution, incubation of the plate (5 min, 37 °C, > 90 % humidity) follows. After 6.5 min the substrate (0.5 g/L 3-indoxyl-3-acetate in aqueous solution with 4 % DMSO) was applied (amount of reagent 580 μL, distribution 0.03 μL/mm2) by spraying. Through active enzyme the substrate is cleaved to indoxyl, which reacts with oxygen to indigo white.
Documentation
With the TLC Visualizer 10 pictures (1 picture/min, exposure time 800 ms) are taken under UV 366 nm. For the evaluation of the effect, the picture after 2 min was used.
Elution from the plate
With the TLC-MS Interface the zone is eluted with methanol for 1 min with a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min
Results and discussion
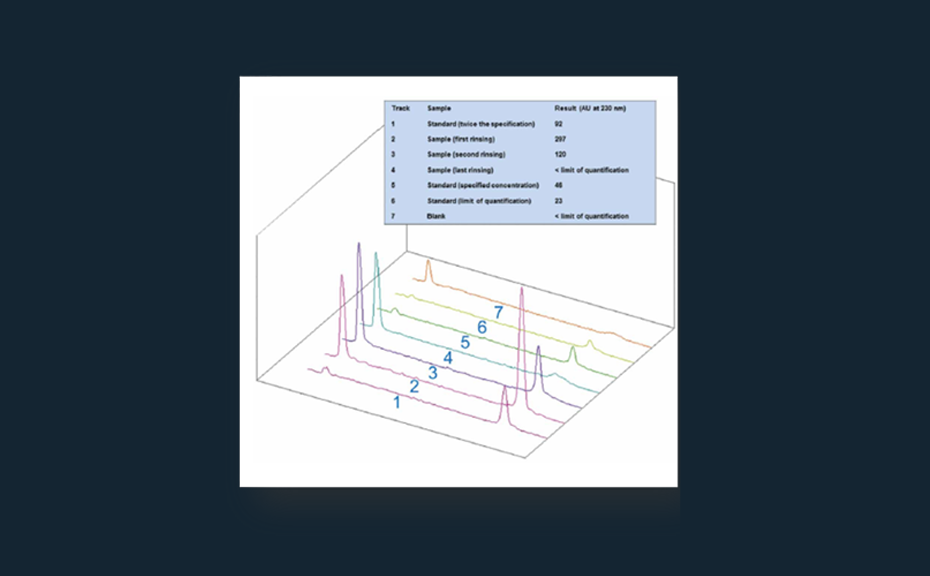
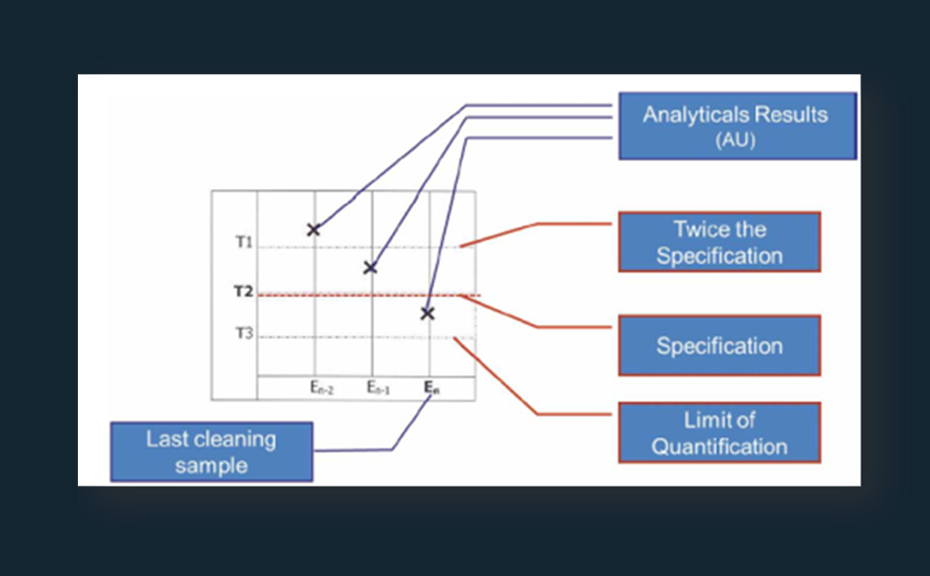
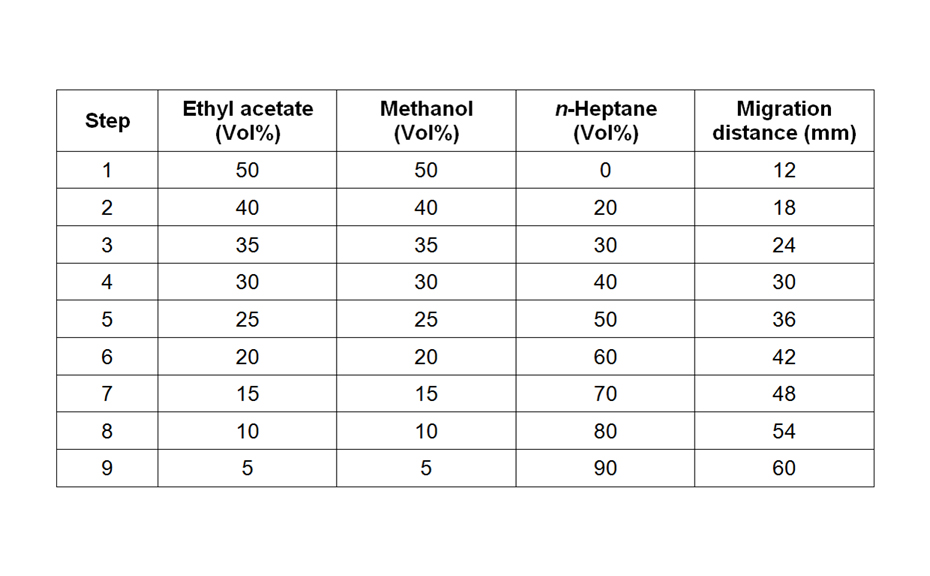
The first separation was performed in the AMD system with a 16-step gradient consisting of methanol (0.05 % formic acid), dichloromethane and n-hexane – achieving a peak capacity of 30. With the development of a dynamic heart cut 2D separation approach the peak capacity was increased. Therefore, the first AMD chromatogram was parted in five equal hRF-ranges. One effective substance was selected and the respective area investigated.
Based on 35 model substances the improvement of separation efficiency was shown. For example, it was possible to distribute seven substances, which occur in the first dimension in the hRF-range of 80–100, through the second dimension to the hRF-range of 7–91.
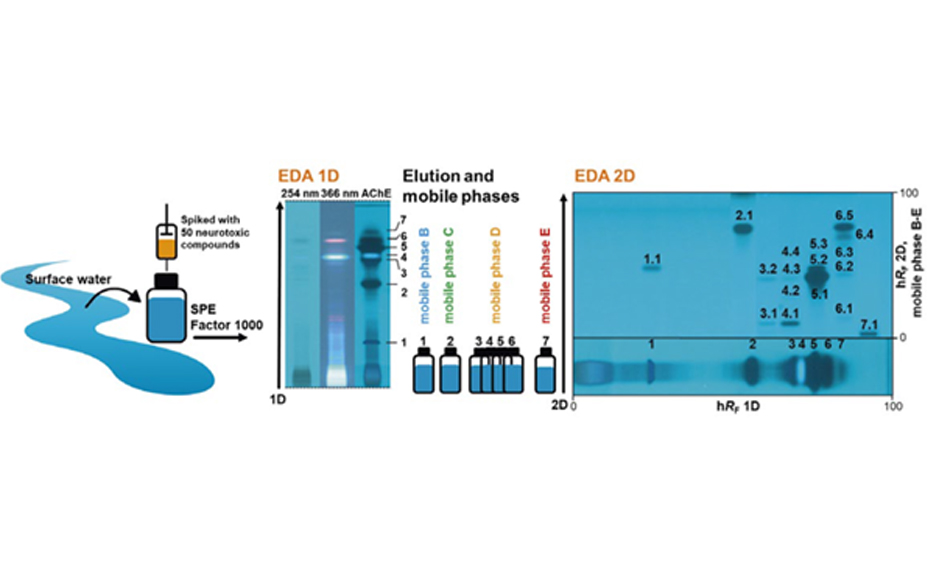
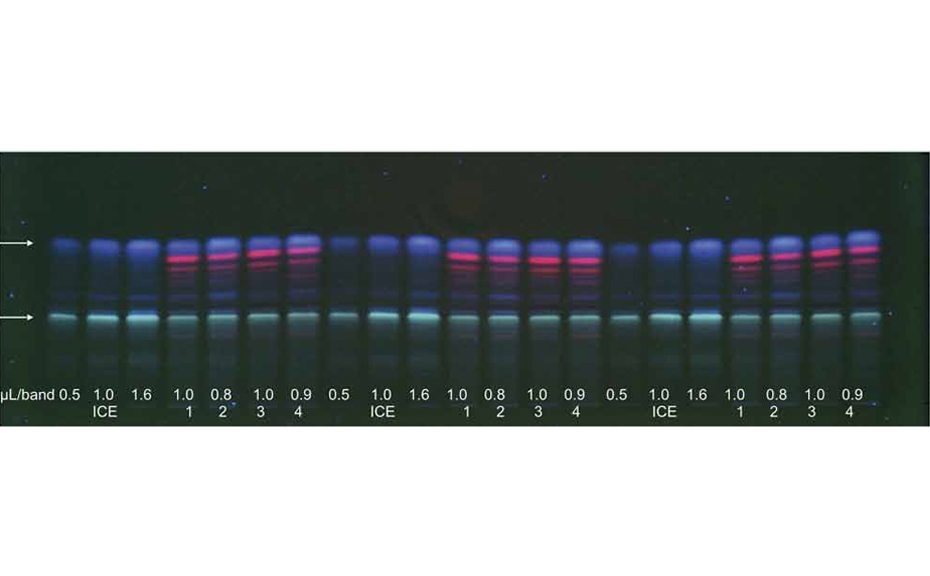
After method development the peak capacity of this dynamic approach was determined based on 125 substances. Therewith a peak capacity of 204 could be achieved, so that separation efficiency could be improved through the factor 7 in comparison to the 1D. The developed approach was applied to 50 AChE-inhibiting substances spiked with surface water sample. After AMD separation and the AChE 4inhibition assay in the 1D seven effective zones were selected. These were eluted and separated in the 2D with respect to the hRF-range adapted mobile phase. With the AChE inhibition assay of the 2D, induced through increased peak capacity, obviously more effective zones could be detected compared to 1D (17 as opposed to 7). More- over it was possible to assign 8 of the effective chromatogram zones clearly to one substance, based on their hRF-values. After 1D the assignment succeeded only for 2 zones.
Through the developed dynamic 2D approach, the peak capacity of EDA could be increased by the factor 7, which enhanced assignment of substances in the spiked surface water. The required time of 2D-EDA of the spiked surface water sample amounted to 8 h. To identify also unknown effective substances in samples, a coupling of this method to further analytical techniques, like MS is possible. Through identification of effective substances, their relevance can be easier evaluated, which is also useful for determination of limit values.
Mass spectra were recorded to characterize the different compounds. The same sodium adduct [M+Na]+ and respective dimer [2M+Na]+ were obtained for both Z/E isomeres. For NMR, the crude product solution was concentrated by a factor of 10, applied (15 μL) on the HPTLC plate, separated, and four zones of each target zone were eluted and combined.
The purification of the crude product (2 kg dissolved in toluene) on a 45-cm column (packed at 40 bars with 40 kg silica gel 60, 15–40 μm, Merck) at a flow rate of 10 L/min with ethyl acetate – methylcyclohexane 9:1 led to a productivity of 20 kg per day. The elution process was monitored online by UV 254 nm detection and in parallel offline by HPTLC.
The different fractions of the target isomer Z were collected and the combined fractions analyzed by NMR. The purity was not sufficient, as the NMR spectrum showed several impurities. Thus, the purification was optimized. The new eluent of dichloromethane – ethanol 19:1 together with a crude product load of 0.5 kg also led to a productivity of 20 kg per day. The purity obtained for the Z isomer was 99.8% with a yield of 88%.
TLC is the best method for development and optimization of purification processes using silica gel. It is simple and allows a rapid upscaling to preparative columns. HPTLC is an efficient tool for offline monitoring of the eluted fractions. Up to 20 fractions can be analyzed in parallel and compared in the HPTLC chromatogram at UV 254 nm, achieving a good overview on the purity and amount of the target compound per fraction.
-
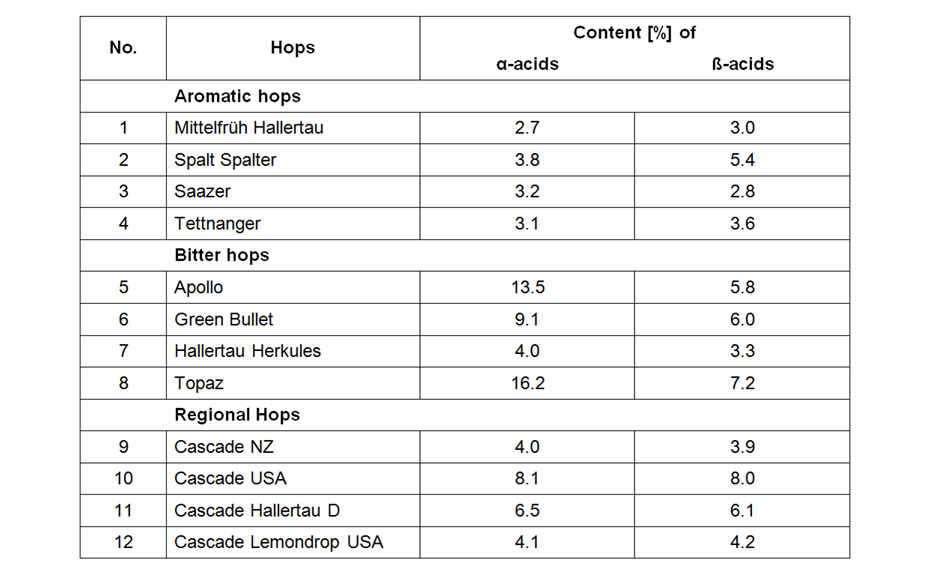
![AMD gradient consisting of methanol – formic acid 100:0,05, dichloromethane and n-hexane [2]](/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/CBS121_Effect-directed-analysis_img2.jpg)
01
AMD gradient consisting of methanol – formic acid 100:0,05, dichloromethane and n-hexane [2]
-
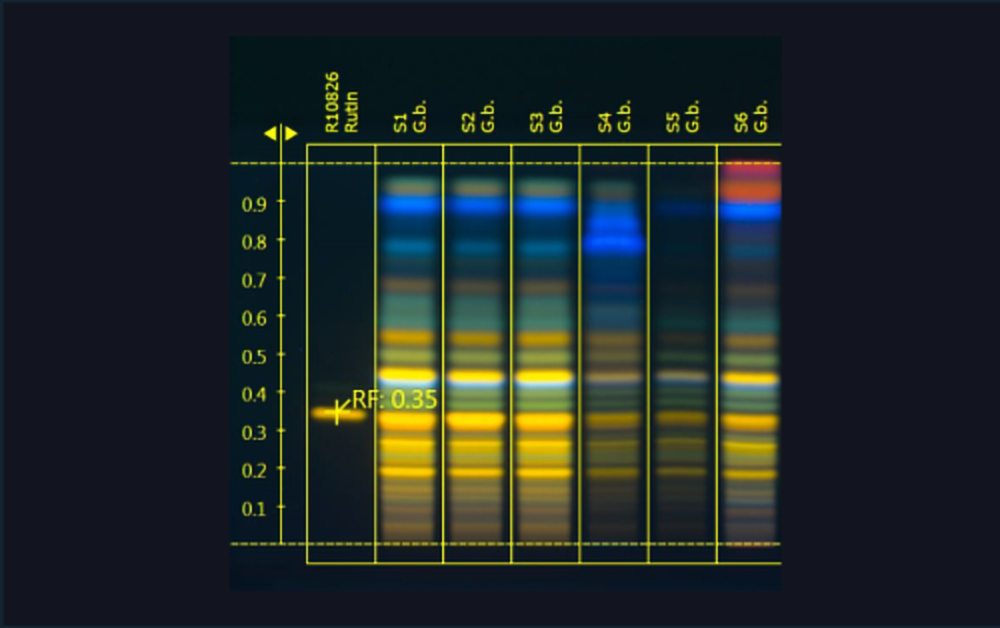
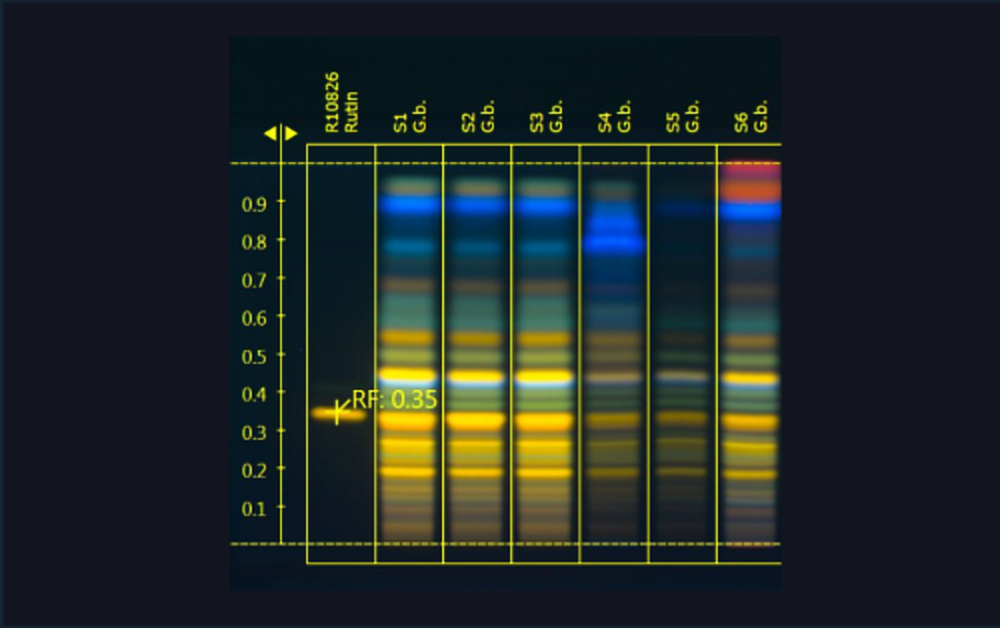
![Image of the dynamic heart cut 2D approach with elution of the chroma- togram zone from the parallel partial HPTLC plate that was only developed (no AChE assay) [2]](/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/CBS121_Effect-directed-analysis_img3.jpg)
02
Image of the dynamic heart cut 2D approach with elution of the chromatogram zone from the parallel partial HPTLC plate that was only developed (no AChE assay) [2]
-
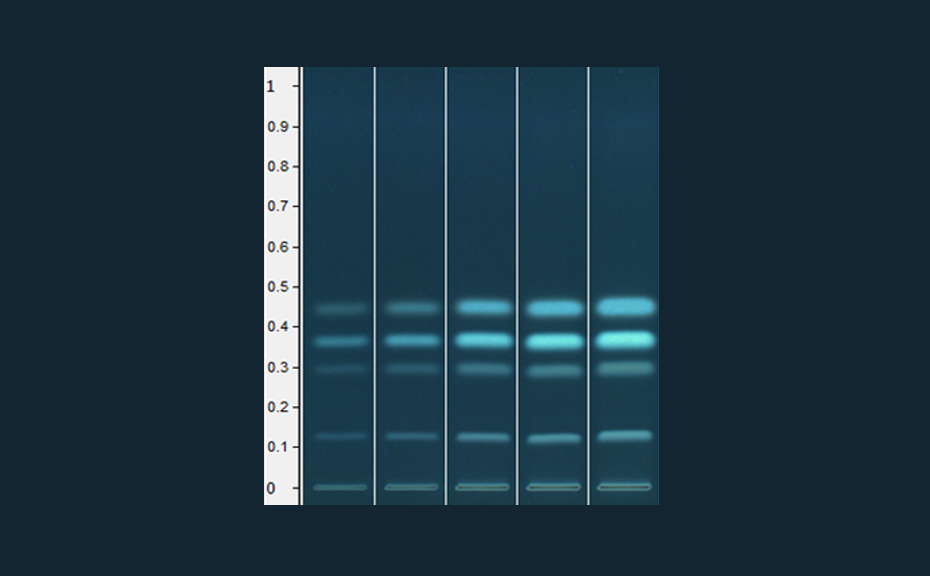
![Spreading of the hRF-range in the 2D, depicted based on 35 model substances [2]](/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/CBS121_Effect-directed-analysis_img4.jpg)
03
Spreading of the hRF-range in the 2D, depicted based on 35 model substances [2]
-
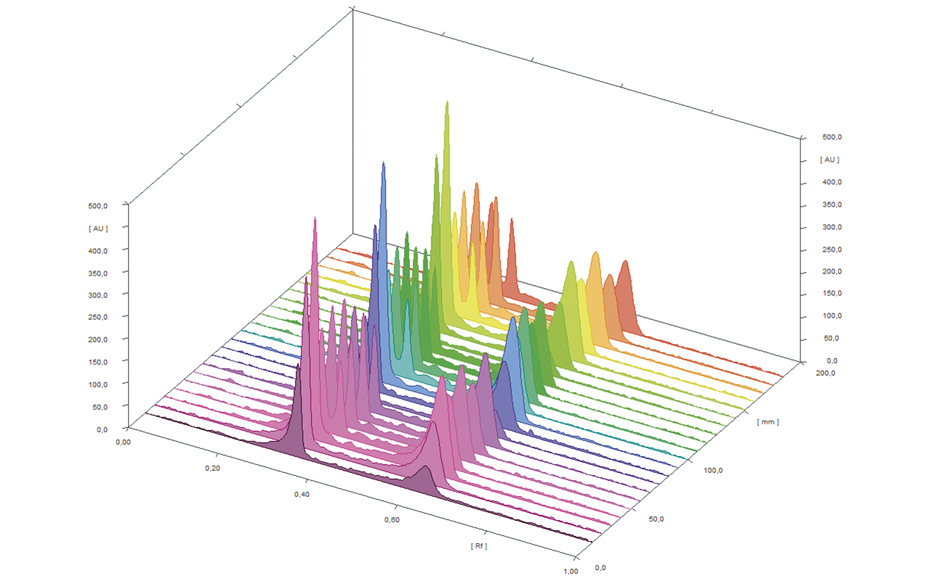
04
Application of the approach for EDA of a spiked surface water sample
Literature
[1] Weber, W. H., et al. CBS 94 (2005) 2
[2] Stütz, L., et al. Journal of Chromatography A 1524 (2017) 273
Further information is available from the authors on request.
Contact: Lena Stütz, Laboratory for Operation control and Research, Zweckverband Landeswasserversorgung, Am Spitzigen Berg 1, 89129 Langenau, Germany, Stuetz.L@lw-online.de







 03
03